What happens in a Bitcoin Network when a transaction is initiated? Find out more!
In our last post, we discussed the core of bitcoin network. It combines some existing concepts like blockchain technology and cryptography hence producing a one of a kind product. This post details on what actually goes around in the bitcoin network when a transaction is initiated.
The misinterpreted fact about bitcoin is that it is complicated because it involves a lot of technical mumble-jumble. The protocol is backed by technology and works on mathematical equations. However, you don’t need to know any of those in order to use bitcoin. Just like you don’t need to know how the car engine operates in order to drive a car. You do need to understand the fundamentals of bitcoin network in order to grasp the uniqueness of the model. How and why it can work, when all the past attempts at digital currency have failed. That is what this post aims to do!
A Virtual Currency
Bitcoin isn’t like cash which can be physically held in your hands. It is a virtual currency representing a secret code: Your Private Key. The private key shows the number of bitcoins that you can spend. It has 64 characters and will look something like this:
E9873D79C6D87DC0FB6A5778633389F4453213303DA61F20BD67FC233AA33262
Note: The private key holds your bitcoin. If your private key is lost, there is no other method through which you can retrieve your bitcoins stored inside your wallet. If your private key gets stolen, the other person can now have full access to your bitcoin funds.
Public Address, Wallets and Bitcoin Address
Now, these bitcoins are stored inside wallets (also virtual). These bitcoin wallets store bitcoins (or essentially the private keys) and are represented using Public Key. The public key acts like a unique identification to your bitcoin wallet.
The public address of a bitcoin wallet is slightly different from a pubic key. As the public key of a wallet is made up of long alphanumerical numbers, bitcoin address is like a smaller, compressed version of the public key. The bitcoin wallet address is similar to a mail address. It can be handed out, whenever you want to send or receive bitcoins in your wallet.
Bitcoin Transaction
In order to understand how a particular bitcoin transaction happens and how it is stored on the blockchain, let’s consider two fictional characters: Aman and Riya for better understanding. Aman, living in US, wants to send 2 BTC to Riya, living in India.
Note: Bitcoin is divisible upto 8 decimal places. The smallest unit of bitcoin is known as Satoshi. 1 Satoshi= 0.00000001 BTC. Currently (in today’s date), the value of 1 BTC is close to 4.5 lakhs.
Aman, currently has 5 BTC in his wallet. His previous transaction consisted of paying 1 BTC to buy a laptop (Output of this transaction will act as input for the next transaction). In order to transfer 2 BTC to Riya, first Aman needs to enter the public address of Riya and the amount of BTC he wants to transfer.
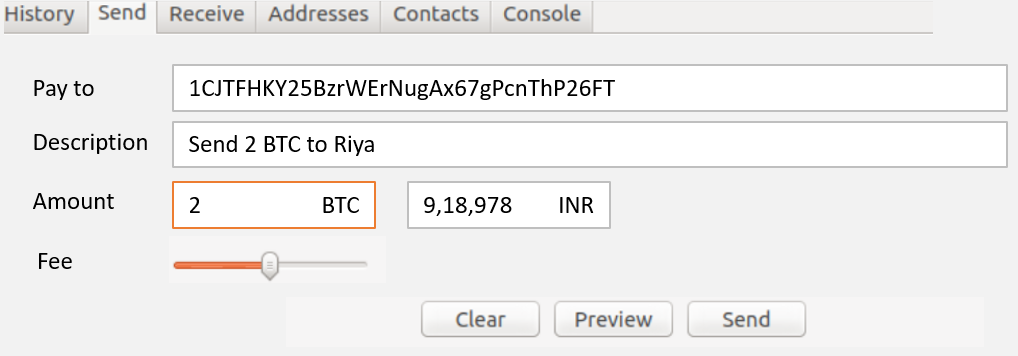
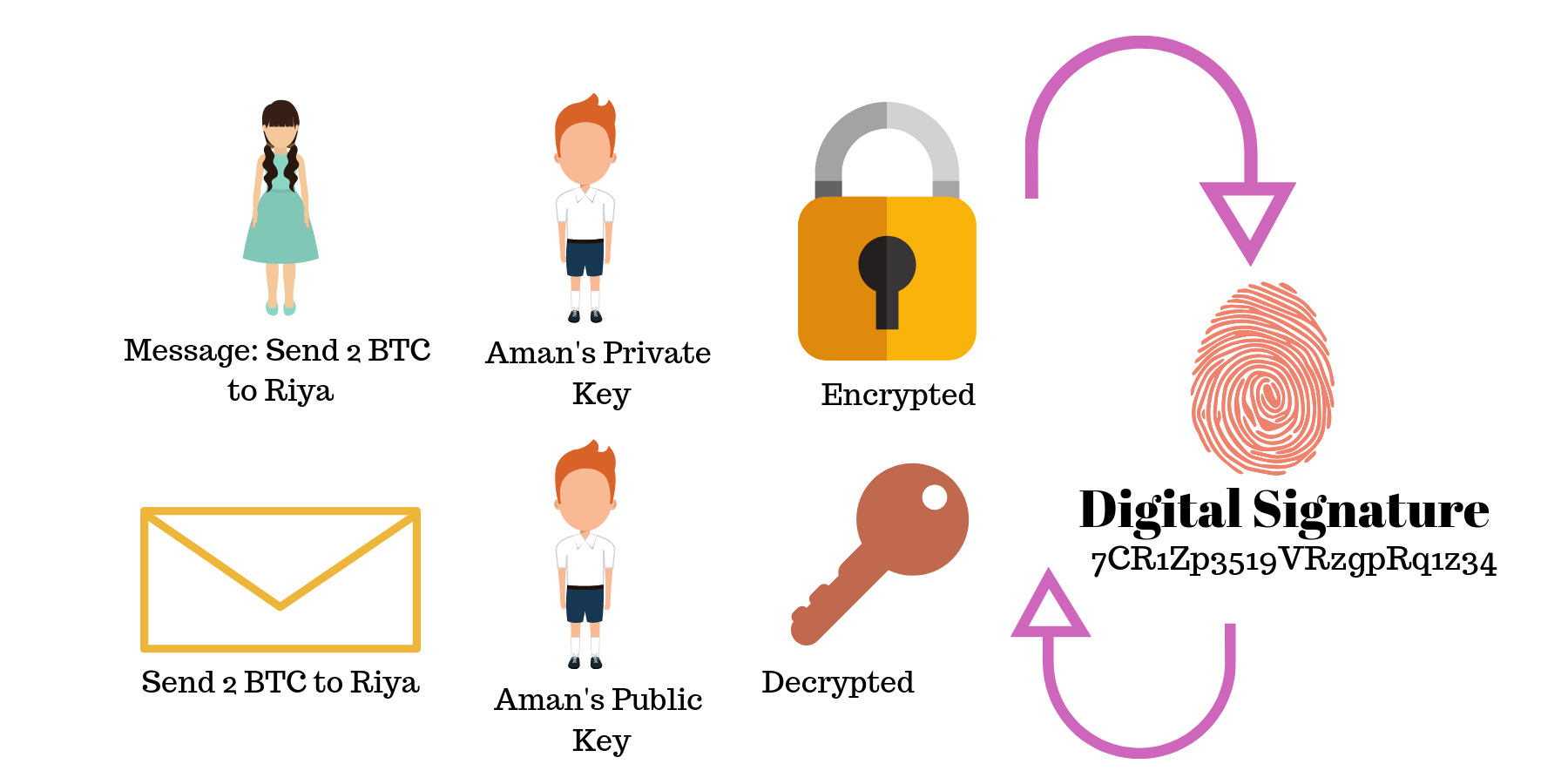
When Aman presses ‘Send’, the bitcoin network will create a digital signature in order to verify the authenticity of the transaction. This digital signature is encrypted with Aman’s private key. Although no one, including Riya, will be able to view Aman’s private key. This digital signature is decrypted by Riya using Aman’s public address to verify that the transaction and message was indeed sent by Aman.
Input and Output in Bitcoin Network
As mentioned before, Aman’s previous transaction consisted of paying 1 BTC to a retailer for buying laptop. Bitcoin’s network utilizes the output of the previous transaction (in our case Aman to laptop retailer) as the input of new transaction (in our case Aman to Riya). This is done in order to verify if the payee has required funds.
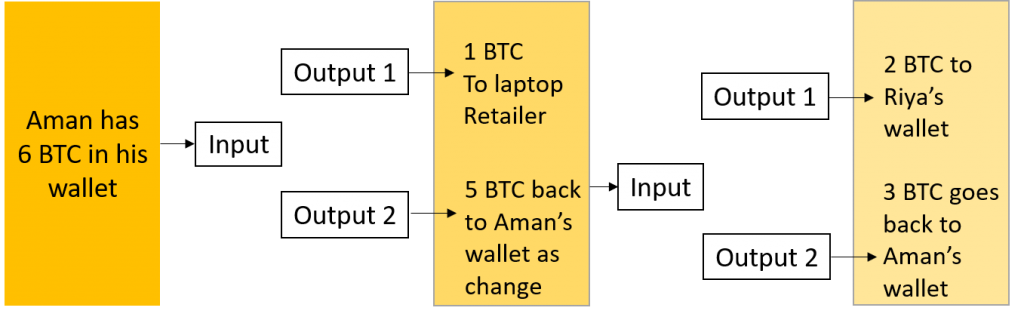
Every time a bitcoin transaction happens, it produces 2 outputs. The new transaction of Aman references to the previous transaction as input. The new transaction creates new output when he transfers his BTC to Riya’s wallet. The unspent amount of previous transaction becomes the input of the next transaction. All of these inputs and outputs are automatically generated through bitcoin network. Aside from having to enter all the details, Aman does not need to do anything. Everything happens behind the scenes of Bitcoin Network

