Exploring 3 different types of blockchain with examples
In our previous class on blockchain technology, we thoroughly decoded what is blockchain and how does it work. This week, we are taking you a step further. We are going to unfold the different types of blockchain, its pros and cons, examples, and use cases.
In case if you are completely unfamiliar with blockchain technology, we would suggest you read Module 1 and Module 2, for a better understanding of this class.
The 3 Blockchain Types
Since Satoshi Nakamoto gave birth to bitcoin, different models of blockchain have emerged. On these models, many new cryptocurrencies have been built.
In this guide, we are going to discuss the three main types of blockchain: Public, Private (Permissioned) and consortium. We are going to discuss the features of these models, pros & cons, as well as present use cases and examples.
What is Public Blockchain?
Just as the name indicates, a public blockchain is accessible and made for all. Anyone, who is a part of the public blockchain can add or read transactions/ data. A public blockchain is completely ruled, managed and maintained by the members of that particular blockchain network. It is an online democratic region- it is for the people, by the people, and of the people.
On a public blockchain, any member, who is a part of the network can transact with one another, read the data or even audit the information. It is an open-source network. Anyone is free to join from any part of the globe. The information on the ledger remains transparent and open to the people of the network
A public blockchain represents the true meaning of decentralization. There is no central authority. Instead, it is completely run by all the people, who are a part of the particular blockchain network.
But, how is that possible? Without any supreme person or entity running the show, how do you ensure that the show will run smoothly, effectively and honestly?
Bitcoin is the greatest example of the greatest public blockchain show- and in some ways.it is running even better than a centralized system.
Bitcoin: An Example of Public Blockchain Type
The digital cryptocurrency bitcoin is open-source public blockchain. Millions of nodes are a part of the bitcoin network, from across the world. There is no central bank monitoring and operating transactions. Instead, the bitcoin bank is run by these nodes, all operating at the same levels to each other with equal power.
The nodes of the network can transact bitcoins with each other. All the transactions are audited and verified by the members/ nodes of the bitcoin blockchain. By consensus mechanism, if maximum members of the network agree to the validity of the transaction, then it is approved. So, in place of a central bank, in bitcoin, we have millions of nodes who verify and approve transactions. This makes the entire system fair and just.
Other examples of public blockchain are ethereum and Litecoin.
Permissioned or Private Blockchain Type

After public blockchain, another emerging blockchain type with restricted and controlled use is Private or Permissioned. The private blockchain is another version of a centralized interface.
In this kind, there are limited users who are a part of the blockchain network. Only restricted users have the rights to write any data on the blockchain. Also, there are limited users, who hold the rights to view the data written on the blockchain. In the case of public blockchain network like bitcoin, millions of nodes have the rights to validate and approve transactions (Consensus Mechanism- those transactions get approved which are validated by maximum nodes). In case of a permissioned blockchain, only a limited few have the powers to approve or validate any transaction or data. Furthermore, unlike a public blockchain, the real identities of entities on a private blockchain remain known.
So, what is the use of such a type of blockchain?
This form of blockchain can be widely used for private enterprise or businesses. In an enterprise, sensitive data such as clients, billings, etc have to protected within the inner circle. Hence, a centralized model with additional security via cryptography, cost-efficient, a distributed database, as well as better scalability in terms of size and speed- are some of the additional benefits for a private blockchain.
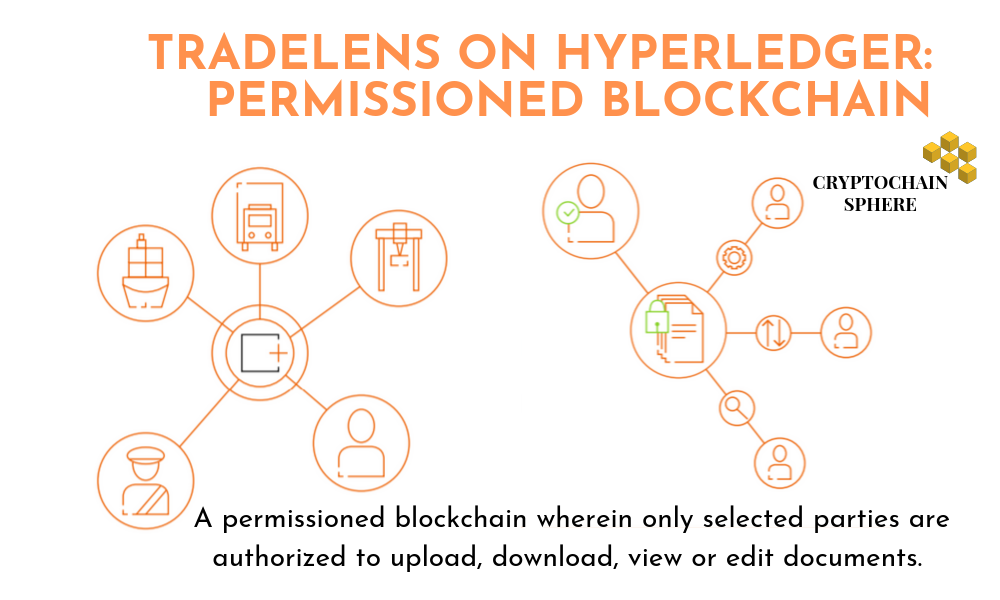
Use Case of Permissioned Blockchain: Tradelens on Hyperledger Fabric
Tradelens, developed on Hyperledger Fabric, is a supply chain platform underpinned by blockchain technology. A blockchain ecosystem involving cargo owners, inland transportation providers, customs and other government authorities, etc- are brought under a shared platform. It is a permissioned blockchain wherein only selected parties are authorized to upload, download, view or edit documents.
Consortium Blockchain
This type of blockchain is a mix of the best characteristics from public and private blockchain. While private blockchain is operated for one entity, consortium blockchain is operated among a group of entities. A number of preselected nodes or users are in charge of the decisions and approvals in the blockchain network.
Consortium blockchain offers enhanced security and auditability than a private blockchain. It is more decentralized when compared to permissioned type but not nearly as decentralized as a public blockchain. A consortium blockchain is also known as a semi-decentralized model.
The latest project of Facebook- the Libra blockchain is sort of a consortium blockchain. There are 28 members, presently appointed in this consortium. These 28 members belong to different organizations such as Mastercard, PayPal, Uber, Vodafone, etc. In the case of Libra coin, 28-member consortium have the powers to approve financial transactions.
Example of Consortium Blockchain: Bank Chain
Bank Chain represents a community of banks which are finding different ways to explore blockchain technology. India’s first blockchain consortium allows different banks to collaborate and build blockchain solutions.
The group of members includes Axis Banks, SBI, ICICI Bank, Kotak bank, DCB bank- are a few names among others. There are several blockchain-based projects which are being explored by the group. One of which is clearchain- focussed on reducing fraud in business lending.
Final Thoughts
Since bitcoin, different models of blockchain have been deployed for different use cases. Depending upon the primary objective of our project- scalability or security- you can deploy the particular type best suited.