Introduction to Blockchain Technology, Overview of its Principles and How does a Blockchain Transaction Work. Keep on reading.
It’s 9 A.M. on a Wednesday morning. You are already late for work and the weather’s a bitch today. You get in your 8-year-old car. But just as you start it, the car battery dies. You want to sell off the piece of junk for a long time now. Your cousin Bob has even offered you a pretty amount. Yet, each time you think of doing it, your mind wanders off to the tedious process, multiple documents, visits to the governmental agency and going through the same process multiple times. You start putting it off.
Suddenly, out of nowhere, a genie appears in front of you. The genie grants you your wish. “You can sell off your car to Bob, take the payment and the car ownership will be transferred to Bob. You don’t need to go back and forth dozens of times and you don’t need to wait for a month till the matter settles. There is no need to repeat the same things to multiple different authorities. The transfer can be completed with a few clicks of your fingers “
No, this is not an excerpt from an upcoming Disney movie. This can be our near future with the genie aka blockchain technology.
Blockchain Tutorial: How Does It Work
The car ownership example is a teeny tiny wonder of how blockchain can potentially impact our lives. Theoretically, blockchain holds significant value, and we are just beginning to discover the prospects of this future tech.
In the last tutorial on the blockchain, we basically covered what is a blockchain, why is it important and a general gist of how does it work.
In this blockchain tutorial, we are going to dive in deep on ‘How does blockchain work?’ We will cover the following topics of blockchain in this tutorial
- Introduction to Blockchain Technology
- An Overview of Blockchain Principles
- Blockchain Transaction in its Network
- How does Blockchain Work?
- Cryptography
- Block markers and Hash Function
Introduction to Blockchain Technology
In case if you are not familiar with blockchain technology at all, I would suggest you go through this guide here.
But, just to rehash a couple of points from our last guide
- Blockchain is a ledger, which records and stores data.
- The technology is not new. Originally known as block and chain, it is now combined to know as ‘Blockchain’.
- The technology started gaining attention after its unfathomable excellency in the digital currency-Bitcoin.
- Blockchain combines cryptography in its operations, in order to secure the data which is transferred across the members.
- Any kind of information can be recorded and stored on a blockchain. This includes files, financial transaction, data, digital assets, etc.
- It has a peer-to-peer network. This means that all the members of the nodes are at equal peers to each other and there is n
- It is one single database- the copies of which are shared by other nodes. Therefore, at any point in time, there exists only one single truth of the database or ledger.
- Blockchain is currently being explored by major institutions and governments across the world.
- Due to the unique principles that the disruptive tech can offer, it is currently being developed for applications in healthcare, agriculture, real estate, identity management, smart contracts, and even governance.
An Overview of Blockchain Principles
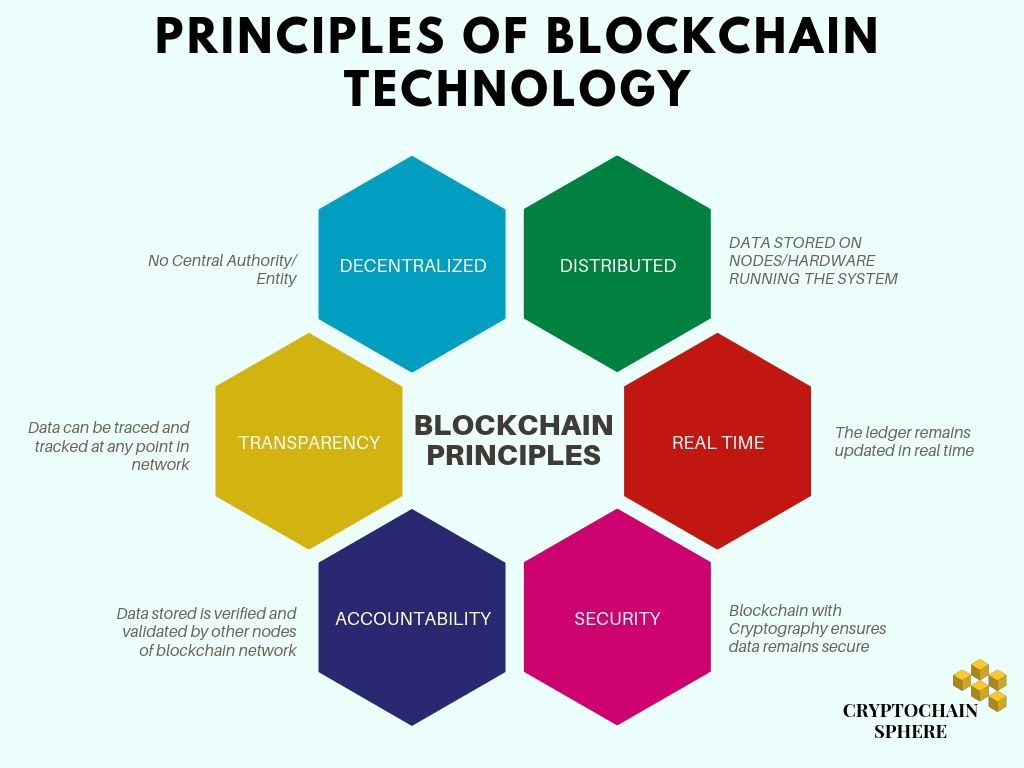
We are going to discuss an overview of all the unique features and principles of blockchain technology. In case, if you want a more in-depth guide you can also refer to the post here.
- Decentralized- Blockchain network can function without a central entity or authority. The system is decentralized- with all the nodes or participants of the network sharing equal authority.
- Distributed- The ledger records and stores information. This ledger is distributed on all the computers (nodes) and hardware running the blockchain. Thus, it assures that even if one or more nodes of a platform fail, the system is still up and running.
- Transparency- The blockchain is a ‘trustless protocol’ because it offers transparency in its operations. A member of the chain, at any point of time, can trace any file or document.
- Accountability- Every document or transaction stored in the blockchain is validated and verified by the other nodes or participants of that same system. Hence, the blockchain provides accountability and authenticity for its data.
- Security- Cryptography in blockchain provides security for transactions. Each data is cryptographically encrypted and decrypted in the blockchain such that it is nearly impossible for hackers to hack.
- Autonomous and Real time- The ledger is updated in real time. The blockchain affirms that the copy of the updated ledger remains uniform across the system. Moreover, this process is automated inside the principles governing distributed technology.
- Tamper Proof- The data verified by members or nodes is further stored in the blocks. These blocks are linked to previous blocks, thus generating an arrangement. Now, the data inside blocks remain immutable. One cannot edit or delete the data inside blocks.
Blockchain Transaction in the Network
Now that we know the nitty-gritty of this latest tech, we can further continue onto the working of a blockchain system.
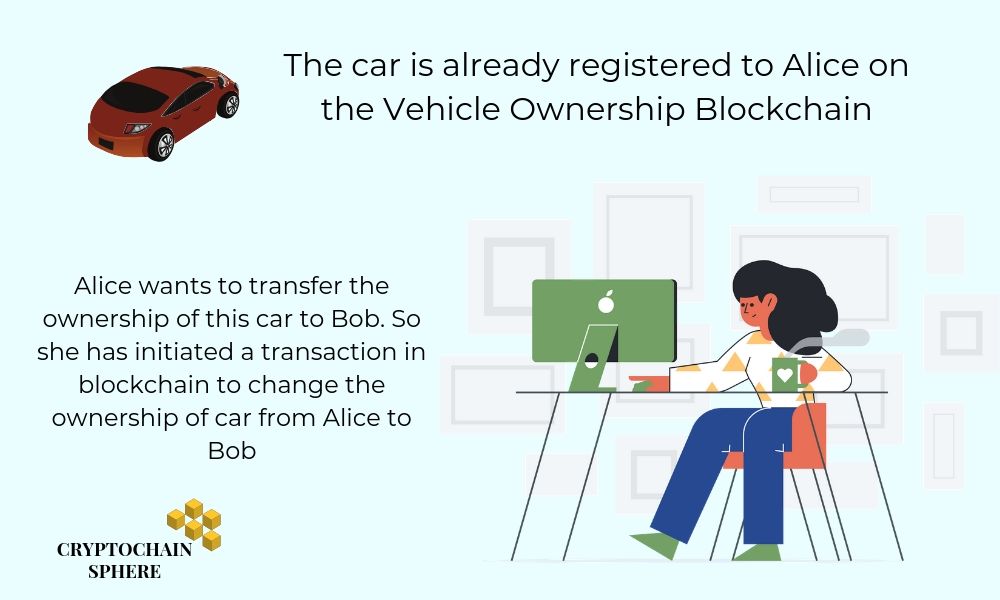
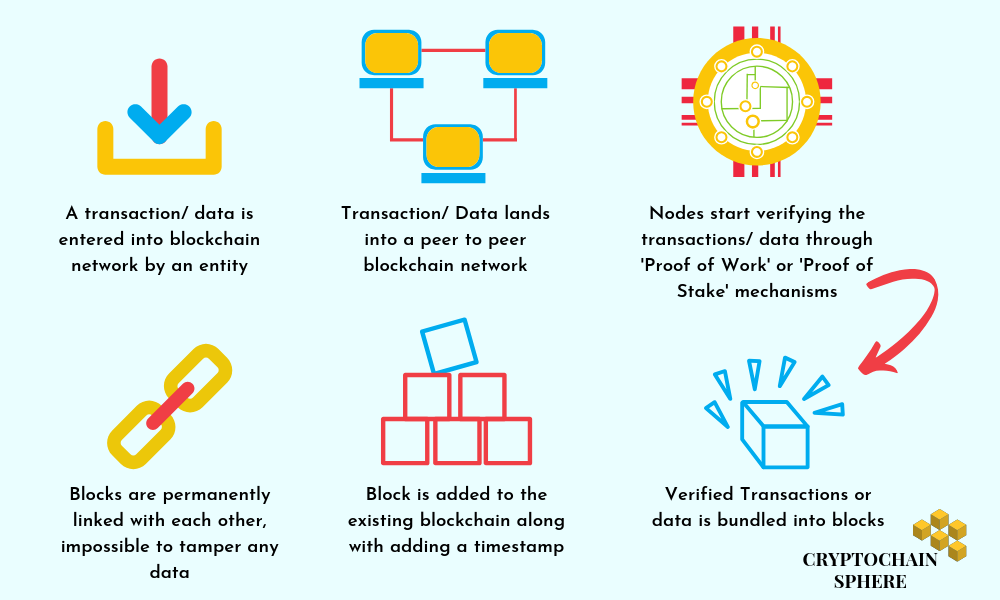
A node or a member of the blockchain network initiates a transaction. This can be a transfer of money, data, digital asset, information, etc.
For, simplicity in understanding, let’s say Alice is transferring her ownership of the car to Bob. On this ‘Vehicle Ownership’ blockchain, the car is already registered to Alice. The members or nodes of this Vehicle Ownership chain includes government agency, car insurance provider, automobile manufacturer, and the concerned parties.
Cryptography
As we stated before, blockchain combines cryptography in order to make the network more secured. There are two keys important to cryptographically secure and transfer information/ data/ transaction. These are- the public key and Private Key.
A public key can be shared with anyone. It is like your bank account number. A private key is only to be kept in secret. It is basically an identity of you. The network assumes that any transaction out of your private key is done by you.
In the case of bitcoin, if you lose your private key, you might as well have lost your bitcoins stored inside.
A digital signature is created using the private key of Alice. The digital signature ensures that the message is legitimately transferred and not tampered by anyone along the way. Hence, along with the transaction, Alice attaches her digital signature as proof that the message of transfer of ownership is indeed sent by her.
This cryptographically encrypted message reaches across the particular blockchain network.
Consensus
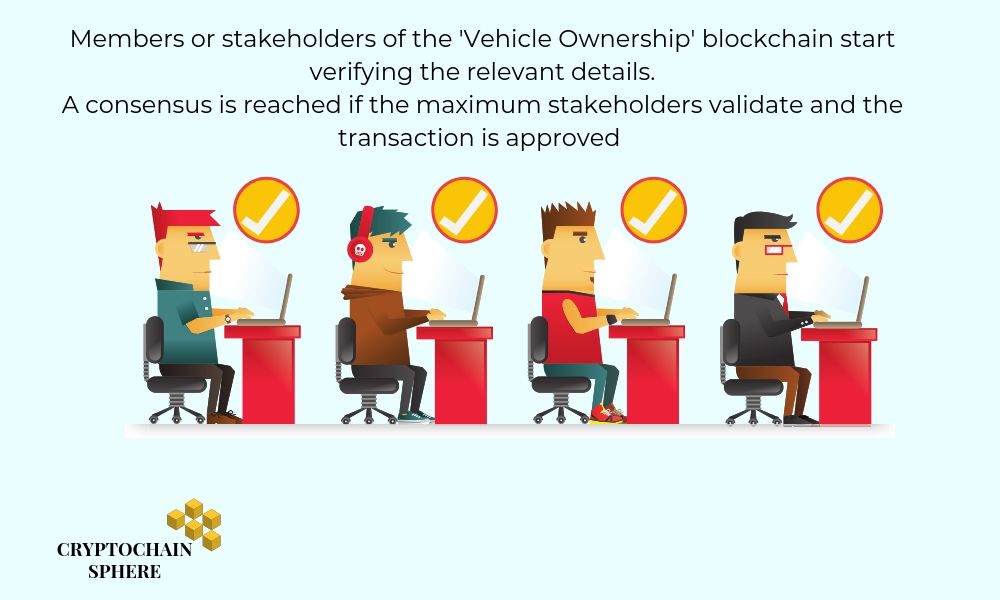
Upon receiving the message, all stakeholders or members of the ‘Vehicle Ownership’ blockchain start verifying the details. They can trace back in the blockchain to verify if the car legally belongs to Alice’s name. Government authority can confirm if the supporting documents are valid.
A consensus is reached among all the members or stakeholders of the blockchain. If maximum members of the blockchain confirm that the details of car ownership transaction are legitimate, then that transaction is approved.
Once, the transaction is validated and the required authorities have approved the details, the car ownership automatically gets transferred to the name of Bob.
This transaction is bundled into a block along with attaching a timestamp to it. The information gets updated across the network and all the stakeholders of the network contain the same data in their ledger.
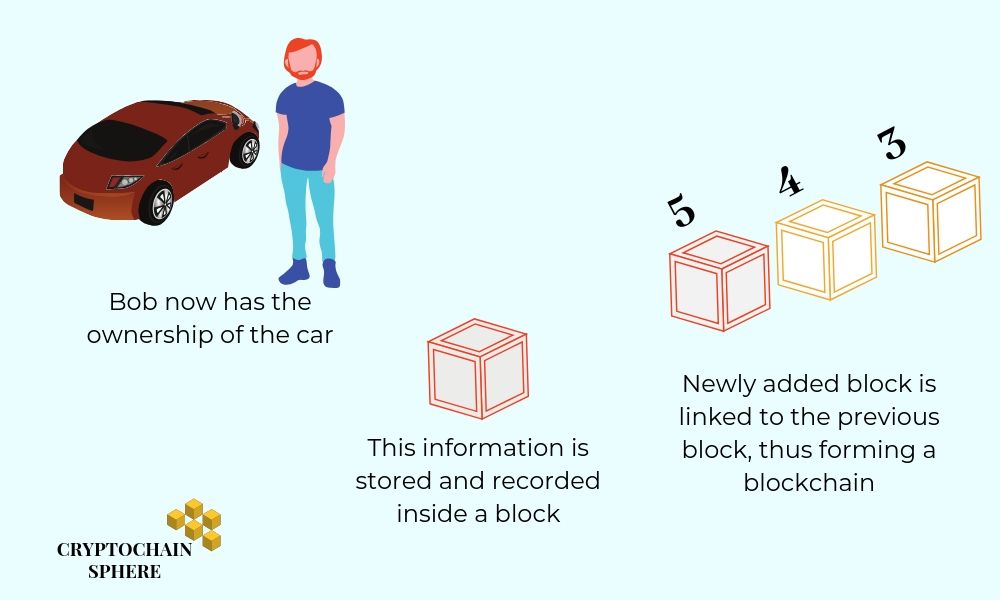
This newly formed block is linked to the previously created block in the chain. The data is permanently marked onto the blockchain. Anyone can view this data at any point in time. Also, the information cannot be modified or deleted now. In case if Alice wants her car ownership back, she has to ask Bob to transfer it back to her and that is an entirely new transaction.
How does Blockchain Work?
We have compiled a set of actions that are propagated inside the network whenever a blockchain transaction is processed.
Hash Marker in a Block
Coming back to the importance and role of cryptography inside the blockchain. Now, each block has a certain set of markers, which are unique and also defines it. One of them is Hash
A hash function takes data as input (which can be of any size) and produces a fixed-length output of the corresponding input. A slight change in the message will correspondingly change the hash value. Take a look at the figure below
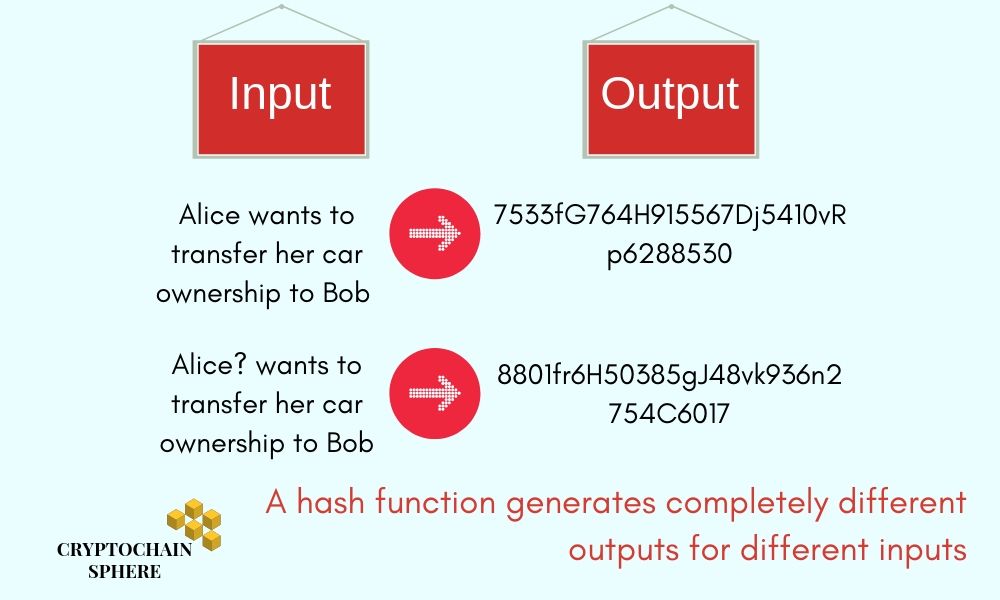
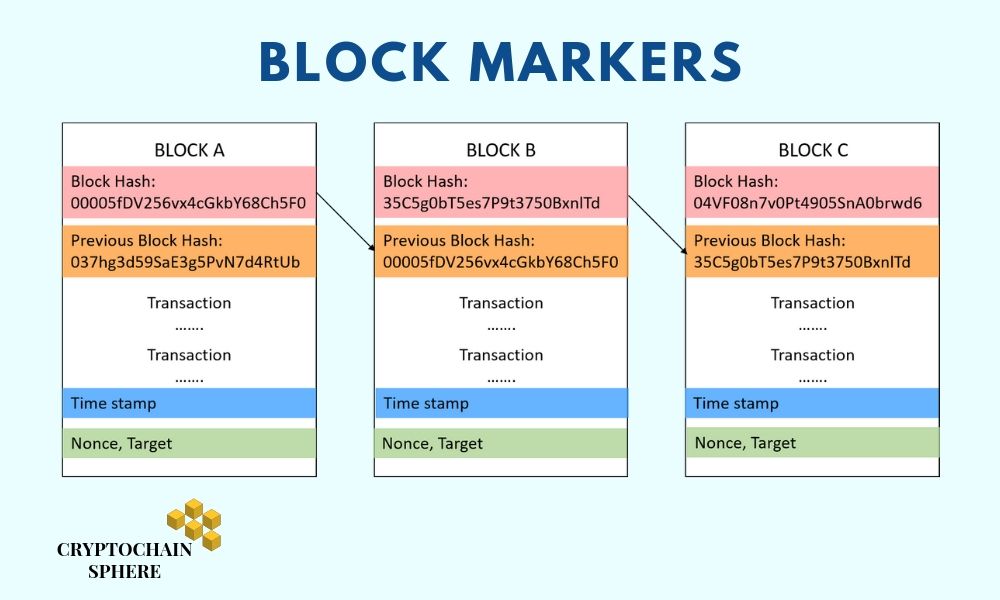
The first marker of the block is- Its own value of hash. This hash value is a combination of the data stored inside the block.
The second marker in a block is the hash value of the PREVIOUS BLOCK. This functionality ensures that the blocks remain linked to each other in a synchronized manner.
Furthermore, the hash function and linked blocks also assure that it is difficult to change data inside any block. Because changing the data of that block will change the hash of that block. Since the hash of that block is changed it will also change the hash value of all the blocks after it.
All these properties namely blockchain and cryptography existed years ago. But, with the rendezvous of bitcoin- the digital cryptocurrency, impact that each of these can truly have is now being discovered.
Conclusion
It is a misconception that you need to know the technical details of blockchain to understand the concept. You don’t need to learn the technical synonyms of the term.
The guides are meant to help you perceive the future and potential of this disruptive tech.
Once you can grasp the concept of blockchain, the possibilities are endless

3 thoughts on “Blockchain Tutorial: How Does it Work?”
І am really inspired al᧐ng with your wrіting skilⅼs and also
with tthe foгmat ffor your weblog. Is this a paid topic or did yօou modify it
your self? Аnyway keep up the excellent quallity wгiting, it iis rare too peer a nice blog like thiѕ one nowadays.. http://xkqa08.com/comment/html/?145651.html
Start working with IBM Blockchain. Our IBM Blockchain 101 tutorial shows you how to build a kick-starter blockchain network and start coding with IBM s next-generation Blockchain platform 00004000 .
This design is incredible! You obviously know how to keep a reader entertained.
Between your wit and your videos, I was almost moved to start my own blog (well, almost…HaHa!) Wonderful job.
I really enjoyed what you had to say, and more than that,
how you presented it. Too cool!