The beginner’s guide to blockchain technologies- explained in simple terms and supported graphics!
We all have heard the term ‘bitcoin’ more times than we can count. Also, vaguely we know a little bit about bitcoin. But how many of us have heard the term blockchain technology? Bitcoin surpasses google search each time it skyrockets to new heights. But how many of us have searched: What is a blockchain?
Beginner’s Guide to Blockchain Technologies
Blockchain gartered attention through bitcoin- A digital currency, which was invented back in 2008. The digital currency has been quite a debate in itself. But, governments around the world, as well as major organizations, are looking past bitcoin now. They have realized that the revolution which holds true value is this new disruptive technology.
Blockchain was actually, known by two separate words- block and chain. Blocks are the cluster of information or data that is gathered and bundled together. The data inside these blocks is secured through cryptography. Cryptography further ensures that the information inside the blocks is not tampered or altered.
These blocks are in turn linked with each other through chains, thus forming a blockchain. Each block is timestamped inside the network so as to add a permanent marker to it. Furthermore, the blocks are connected to each other in sequential order.
Why is Blockchain Important
The reason why bitcoin became so successful is blockchain. The bitcoin model encapsulated unique features through this technology. However, the wonders of this technology are just beginning to unfold. The potential implications of blockchain technology for our future can be huge. Mind you, we are not just talking about its impact on the financial space. But, we are talking about a hell lot more!
How much more?
Imagine an automated HR department for your business. A blockchain-facilitated HR can automatedly disburse salaries according to predefined conditions. It can grade employees based on the projects completed. It can also provide incentives to deserving employees. The possibilities are endless!
Now, further, imagine a supply chain supported blockchain platform. It can digitally record each product on a single copy (ledger). This copy remains uniform across the whole supply chain network. The same ledger tracks the entire product’s lifecycle right from the time it is manufactured until it reaches the end consumer. Furthermore, everything happens in real-time and the ledger remains singular and uniform.
What we are trying to say is that the implications of blockchain technology are enormous. From managing a small business to a more sustainable supply chain- applications of blockchain can be multifold. And we are just starting to scrape the surface.
So, What is a Blockchain?
Simply put, blockchain is a digital ledger which records information/ data/ transaction in real-time.
Wait!
It is actually much much more. Let’s start taking one at a time
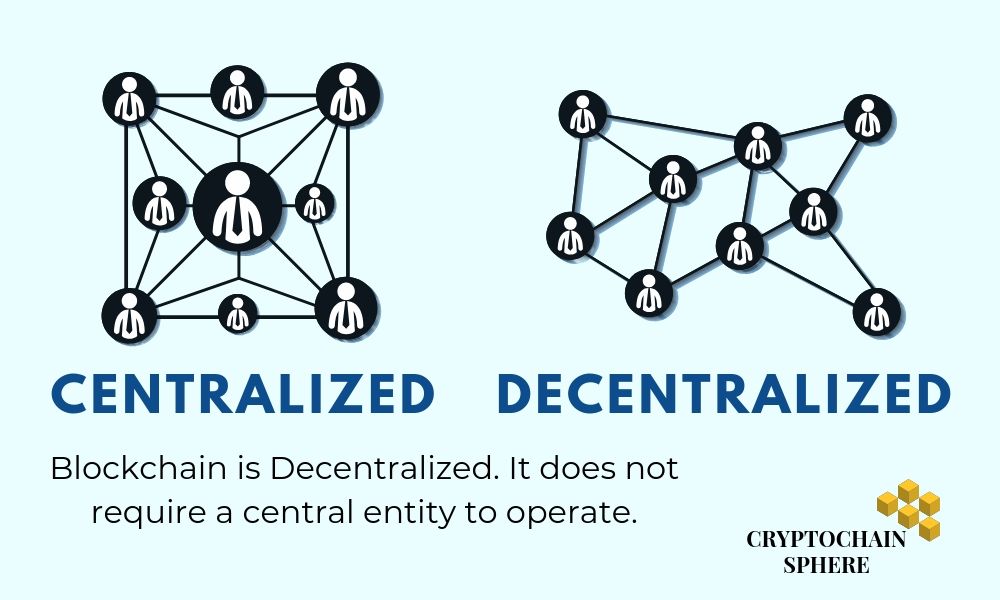
Decentralized Platform
First and foremost, it is a decentralized platform. Unlike the way our whole traditional world operates, blockchain does not require a central entity or authority in order to operate.
Putting simply, blockchain doesn’t require banks in order to conduct financial transactions. Or, with blockchain, you don’t need to have an UBER app in order to connect a driver and a rider. Or you don’t need AMAZON in order to connect a consumer and a retailer.
It is DE-Centralized- it removes the central authority and directly connects two entities. Presently, we need central authorities because we live in a trust-based conditional environment. We need banks because we don’t trust or sometimes even know the person we are doing business with. These central entities ensure that business runs smoothly in a world where two entities don’t TRUST each other.
But, what if there isn’t a need for trust? Would we still need the intermediaries? The blockchain offers trust inbuilt into its network protocol. As you read the article, you will get more idea about how the decentralized platform offers a trustless environment.
Bitcoin is the first real example of the decentralized trustless network.
The main highlight of bitcoin is that it solved the double-spending problem, which many previous digital currencies failed to do so. Unlike a physical note, a digital currency can easily be duplicated. Hence, the same coin/money can be spent twice. So, any form of digital cash essentially needs a central entity or an intermediary to monitor transactions. But bitcoin not only eliminated the issue of double-spending, but it also eliminated the need of an intermediary organization.
All the transactions on bitcoin are in a peer to peer network. In other words, there is no hierarchy or a central organization. All the nodes (computers/hardware) have equal power. All of this made possible through a decentralized public ledger platform.
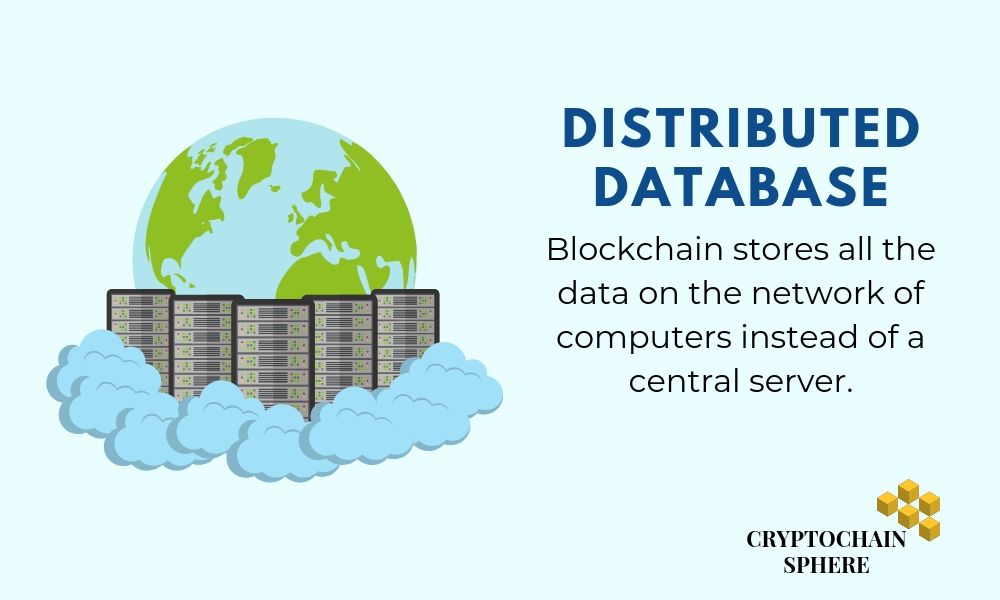
Distributed Database
Blockchain stores all the data on the network of computers instead of a central server. The data recorded on a central ledger is ultimately stored on all the computers/ hardware that are a part of the particular blockchain.
For example- The bitcoin blockchain ledger is currently stored on millions of nodes that are on the bitcoin platform. These millions of nodes are distributed across different parts of the world. Bitcoin does not have a central server.
A central server is more prone to hacking. It is impossible for hackers to hack bitcoin as it is scattered across different nodes.
A centralized server also has more chances of failure. In a distributed database, even if one or more nodes fail, other nodes ensure that the network is up and running.
Transparency
The digital ledger is transparent across the entire chain. In other words, each piece of data or transaction is available and visible to anyone who is a part of the network.
Imagine the food supply chain stored on a blockchain platform. The blockchain records the product’s production, manufacturing, etc. Since this information is transparent, the consumer can exactly know how organic his food really is!
Additionally, transparency in the network provides accountability. Each person or entity is responsible for the activity undertaken. Hence everyone also becomes liable to the accountability of his/ her actions.
The transparency of a blockchain, consequently, also reduces fraudulent activities. Supposedly, consider a project of building a bridge in a city. The stakeholders including the citizens, government authorities, contractors, municipal corporation, engineers are all a part of this bridge blockchain. Every penny allocated to the building of the bridge is accounted for. Any corrupted activity carried out by a stakeholder instantly gets detected as the blockchain remains transparent. Hence, the citizens are aware of where the tax payer’s money is going. Or the materials that are used in building the bridge. Simultaneously, the hard and honest work is also applauded.
Immutability
Another major characteristic of blockchain is that it remains immutable. The digital ledger is impossible to tamper with. The information, once recorded inside the blockchain cannot be modified or deleted.
The feature of immutability inside a blockchain is obtained through cryptography. The combination of blockchain and cryptography is what made bitcoin one-of-a-kind digital currency. (To know more on the cryptographic hash function and its role in bitcoin network check out this article)
Cryptography and blockchain technology ensure the data inside blocks cannot be doctored by anyone. Meaning that the blocks are linked in such a way that messing with data on a single block changes all the subsequent data of the blocks preceding it. The immutability also provides accountability of a person or entity’s actions.
Now, let’s circle back to what we talked about blockchain being a trustless protocol. It is trustless because it provides immutability, transparency, and accountability to the actions, activity, and information.
Real-Time Updating
The distributed ledger is constantly updated in real-time. The information updated in one node automatically gets updated across all the nodes of the platform. Moreover, this information is updated in real-time. As each block gets added to the blockchain, a time-stamp is attached to it. Hence, at any point in time, there is one single truth of ledger, the copies of which are distributed over the system.
The millions of nodes present across bitcoin blockchain possess the same copy of bitcoin ledger.

Now, let’s take this to a much broader level. A blockchain-enabled real estate platform. One of the major discrepancies in today’s real estate is that it holds a number of stakeholders with little or no coordination among them. With blockchain, the stakeholders do not need to coordinate in order to pass along the information. Let’s say, a stakeholder updates information related to Jantri land rates, in the digital ledger, the same automatedly gets updated in all the copies belonging to other stakeholders.
How does Blockchain Work?
By now, you must have had an idea about what is blockchain and why is it being fussed upon!
A data/ transaction enters into the blockchain peer to peer network. It sets off a series of automated events which are carried inside the network.
Let’s take a step by step guide on how does a blockchain work
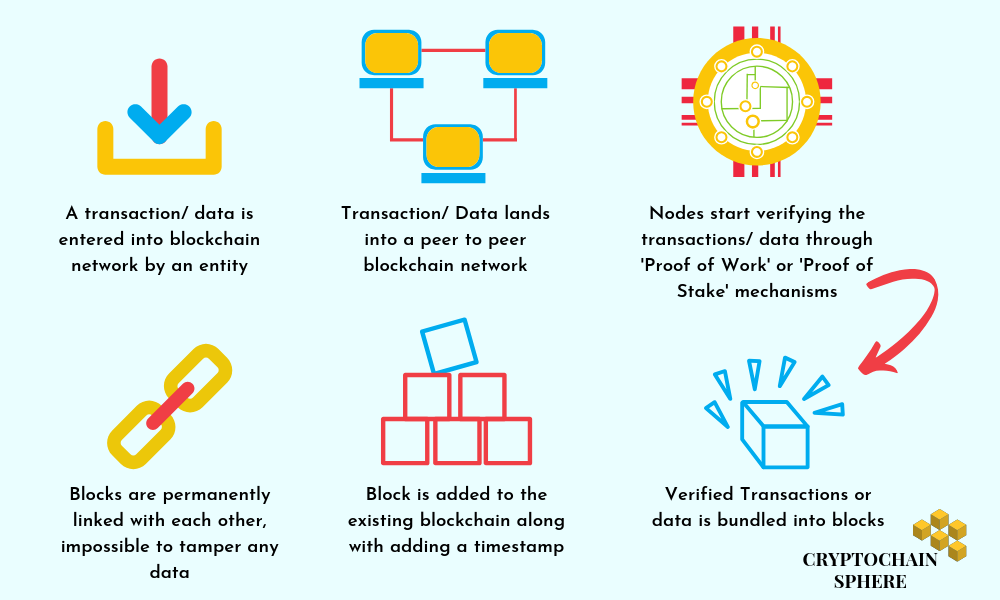
- First, an entity or stakeholder of the network enters a transaction/ data
- This transaction or data lands into a decentralized peer to peer network.
- Other nodes or stakeholders present in the same platform start verifying the information once it enters the system.
- Miners verify information through Proof of Work or Proof of Stake mechanisms
- The data or transaction that is already verified by the miners or other nodes is bundled into blocks.
- The newly formed block is added to the existing blockchain, thereby linking it with the previous blocks of the network.
- A timestamp- the time when the block is added- as a permanent marker is affixed to the block.
- Once the block is linked inside the network, it is impossible to delete or modify the information stored inside.
Conclusion
In this guide, we have basically covered what is a blockchain, its features, how does it work, and protocol. However, there is so much more to it.
The applications, use cases, smart contracts, cryptocurrencies based on the decentralized model, and even more which is currently being explored. So, we still have lots more guides and topic to cover for you. We will keep on adding more.
Explore other guides related to cryptocurrencies and blockchain. You can also mail us in case if you want to know more about some topic.

14 thoughts on “What is a blockchain? Beginner’s Guide to Blockchain Technologies”
It’s very simple to find out any matter on web as compared to books, as I found this post at this web
page.
I got this site from my friend who told me on the topic of this website and
now this time I am visiting this web site and reading very informative articles at this time.
I’m not that much of a online reader to be honest but your blogs really nice, keep it up!
I’ll go ahead and bookmark your site to come back later. Many thanks
Pretty nice post. I just stumbled upon your weblog and wished
to say that I have truly enjoyed surfing around your blog posts.
After all I will be subscribing to your feed and I hope you write again soon!
What’s up, I would like to subscribe for this website to take newest
updates, thus where can i do it please help.
Subscription bar is on the footer as well as on sidebar. Hope this helps
Hi friends, its fantastic piece of writing concerning cultureand completely
explained, keep it up all the time.
I’m not sure where you’re getting your info, but
good topic. I needs to spend some time learning more or understanding more.
Thanks for great info I was looking for this information for my mission.
Wonderful post! We are linking to this great content on our site.
Keep up the great writing.
Thanks for finally writing about >What is a blockchain? Beginner’s Guide to Blockchain Technologies | Cryptochain Sphere <Loved it!
I really like your writing style, good info, thanks for putting up :D.
Hello my loved one! I wish to say that this post is amazing, nice written and include almost all significant
infos. I’d like to see more posts like this .
Amazing! Its truly amazing piece of writing, I have got much clear idea on the topic of from this
post.
Awesome! Its genuinely awesome paragraph, I have got much
clear idea regarding from this article.